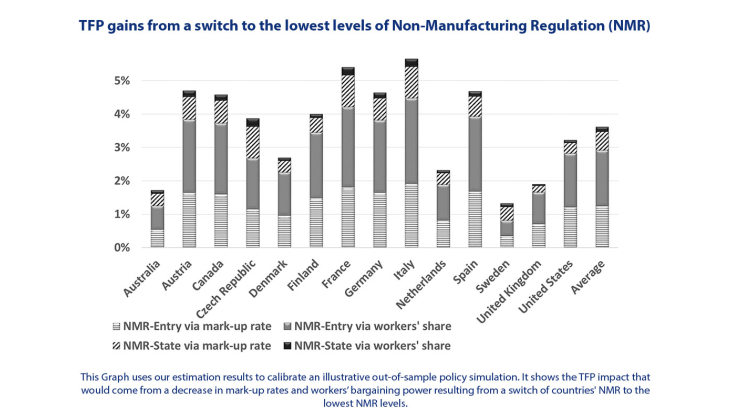
Working Paper Series no. 674. Gilbert Cette, Jimmy Lopez & Jacques Mairesse propose an analysis of new measures of rent creation or (notional) mark-up and workers’ share of rents on cross-country-industry panel data. While the usual measures of mark-up rate implicitly assume perfect labor markets, their approach relaxes this assumption, and takes into account that part of firms’ rent created in an industry is shared with workers to an extent which can vary with their skills. Their results are based on a cross-country-industry panel covering 14 OECD countries and 19 industries over the 1985-2005 period. In a first part of the analysis, authors draw on OECD indicators of product and labor market (anticompetitive) regulations to test how they are related to our new measures of mark-up and rent-sharing. They find that anti-competitive Non-Manufacturing Regulations (NMR) affect mark-up rates positively, and hence firms’ rent creation and workers’ share of rent, whereas Employment Protection Legislation (EPL) has no impact on rent creation, but boosts workers’ wages per hour. However, they observe that these wage increases are offset by a negative impact from EPL on hours worked per output unit, leading to a non-significant impact of EPL on workers’ share of rents. The effects of EPL for low-skilled workers appear to be more pronounced than those for medium-skilled workers, both being much greater than for highly-skilled workers. In the second part of the analysis, Cette, Lopez & Mairesse estimate the impacts of their new measures on Total Factor Productivity (TFP) in the framework of a straightforward regression model. They use the OECD regulations indicators as relevant instrument to take care of endogeneity and to make sure that the resulting estimates assess the proper regulation impacts of rent creation and sharing without being biased by other confounding effects. They find that less competition in the product and labor markets as assessed by our measures of mark-up and workers’ share of rents have both substantial negative impacts on TFP.
Banque de France - Menu Principal
Appuyez sur Entrée pour lancer la recherche